In the rapidly evolving landscape of online gaming, maintaining a reliable and secure game server is essential for providing players with a seamless experience. Unfortunately, one of the most significant threats to game servers today is the Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. This article will explore what DDoS attacks are, how they affect game servers, and most importantly, the strategies you can implement to prevent them.
Understanding DDoS Attacks
What is a DDoS Attack?
A DDoS attack involves overwhelming a targeted server, service, or network with an excessive amount of traffic, rendering it unable to respond to legitimate requests. The “distributed” aspect of a DDoS attack means that the attack is launched from multiple compromised computers, often part of a botnet. These botnets can consist of thousands or even millions of devices, making DDoS attacks exceptionally potent and difficult to defend against.
For a deeper understanding of DDoS attacks, you can refer to the Wikipedia page on DDoS Attacks.
How DDoS Attacks Affect Game Servers
DDoS attacks can have devastating consequences for game servers and their players. Here are some of the primary impacts:
- Downtime: When a game server is targeted, it can become completely unresponsive, leading to significant downtime. Players will be unable to connect or may experience severe lag, causing frustration and dissatisfaction.
- Loss of Revenue: For game server operators, downtime can directly translate to financial loss, particularly for those running commercial servers. Players may seek alternatives if they experience frequent disruptions.
- Damage to Reputation: Continuous DDoS attacks can damage a server’s reputation within the gaming community. Players may leave negative reviews and choose not to return, leading to a decrease in player base.
- Increased Operational Costs: Mitigating DDoS attacks often requires additional resources, such as hiring security experts or investing in specialized DDoS protection services, increasing operational costs for server operators.
How DDoS Attacks Are Executed
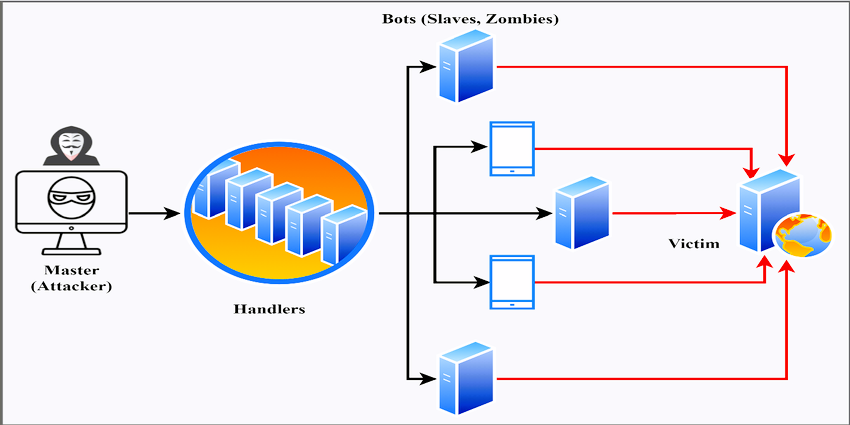
Understanding how DDoS attacks are executed can help you implement more effective prevention measures. Common methods include:
- HTTP Flood: This attack sends numerous HTTP requests to overwhelm a server, exploiting vulnerabilities in the web application layer.
- SYN Flood: This technique targets the TCP connection process, sending a high volume of SYN requests to a server and leaving it unable to establish legitimate connections.
- UDP Flood: In this attack, a large number of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets are sent to random ports on a server, forcing it to respond with ICMP Destination Unreachable packets, consuming its resources.
- Amplification Attacks: Attackers use publicly accessible servers (like DNS servers) to send a much larger response to the target server than the original request, effectively amplifying the attack’s impact.
Prevention Strategies for DDoS Attacks
While it may not be possible to completely eliminate the threat of DDoS attacks, there are several strategies that game server operators can implement to significantly reduce the risk and impact of these attacks. Did you like the article? Read also about Custom Game Events.
1. Use DDoS Protection Services
One of the most effective ways to safeguard your game server against DDoS attacks is to invest in specialized DDoS protection services. These services monitor traffic to identify and mitigate potential attacks in real time. Some reputable DDoS protection providers include:
- Cloudflare: Offers a range of DDoS protection and web security services, including a Web Application Firewall (WAF).
- Akamai: Provides comprehensive DDoS protection solutions that scale to handle massive traffic surges.
- Imperva: Offers advanced DDoS protection along with bot mitigation and security for applications.
2. Implement Rate Limiting
Rate limiting is a technique that restricts the number of requests a user can make to a server within a specified timeframe. By implementing rate limiting, you can help prevent a single user or bot from overwhelming your server. This strategy is particularly effective against certain types of DDoS attacks, such as HTTP floods.
3. Optimize Server Performance
Improving server performance can make it more resilient to DDoS attacks. Consider implementing the following optimizations:
- Load Balancing: Distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers can help prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed during an attack.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Using a CDN can reduce the load on your game server by caching content closer to players and serving it from multiple locations.
- Resource Allocation: Ensure your server has sufficient resources (CPU, RAM, bandwidth) to handle spikes in traffic, even during an attack.
4. Regular Software Updates

Keeping your server software up to date is crucial for security. Regular updates often include patches for known vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit during a DDoS attack. Ensure that your operating system, server software, and any installed plugins or mods are kept current.
5. Monitor Traffic Patterns
Continuous monitoring of traffic patterns can help identify potential DDoS attacks before they escalate. Set up alerts for unusual traffic spikes or patterns, allowing you to respond quickly. Tools such as Wireshark or Nagios can be helpful for network monitoring and analysis.
6. Educate Your Team
Ensure that everyone involved in server management understands the threat of DDoS attacks and knows how to respond effectively. Conduct regular training sessions to keep your team informed about the latest DDoS prevention strategies and technologies.
DDoS attacks pose a significant threat to game servers, impacting both players and server operators. However, by understanding the nature of these attacks and implementing robust prevention strategies, you can safeguard your server against potential disruptions. Investing in DDoS protection services, optimizing server performance, and staying informed about the latest security practices are essential steps in maintaining a reliable and secure gaming environment.